ADVERTISEMENT
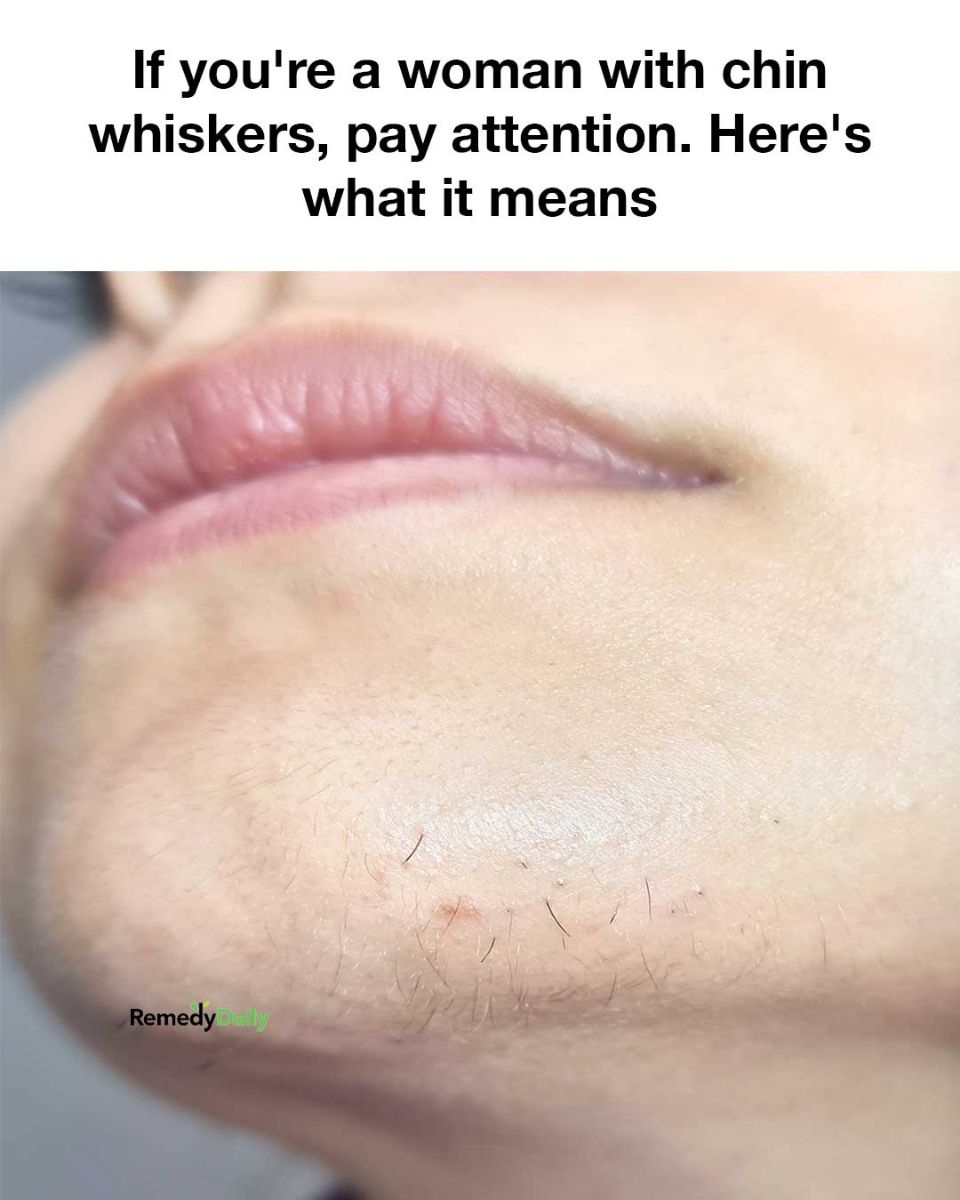
Chin whiskers in women, often a source of concern, are more common than many realize. These facial hairs can vary in texture and color, ranging from fine and light to coarse and dark. While some women may notice only a few stray hairs, others might experience more pronounced growth. Understanding the underlying causes of chin whiskers is crucial for managing them effectively. It’s important to recognize that chin whiskers are a normal part of life for many women, and they can be influenced by a variety of factors including hormonal changes, genetics, and certain medical conditions.
The Science Behind Chin Hair Growth
Hair growth on the chin, like all body hair, is influenced by the hair growth cycle which includes the anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting) phases. Androgens, a group of hormones that includes testosterone, play a significant role in stimulating hair growth. Women naturally produce androgens, but an imbalance or increased sensitivity to these hormones can lead to more noticeable facial hair. The density and distribution of hair follicles, which are determined genetically, also affect how much hair grows on the chin.
Hormonal Factors Contributing to Chin Whiskers
Hormonal fluctuations are a primary cause of chin whiskers in women. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to elevated androgen levels, resulting in hirsutism, which is excessive hair growth in areas where men typically grow hair. Menopause is another period when women might notice an increase in facial hair due to a decrease in estrogen levels, which can alter the balance of hormones. Birth control pills and other medications that affect hormone levels can also contribute to changes in facial hair growth.
Continued on the next page
ADVERTISEMENT